Assessing Bacterial Communities in Bulk Soil and Rhizosphere Associated with NPK Fertilizer in Oil Palm Seedlings via Amplicon Sequencing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22452/mjs.vol44no2.3Keywords:
Palm oil, fertilizer, bacterial communities, amplicon sequencing, Oil palm seedlingsAbstract
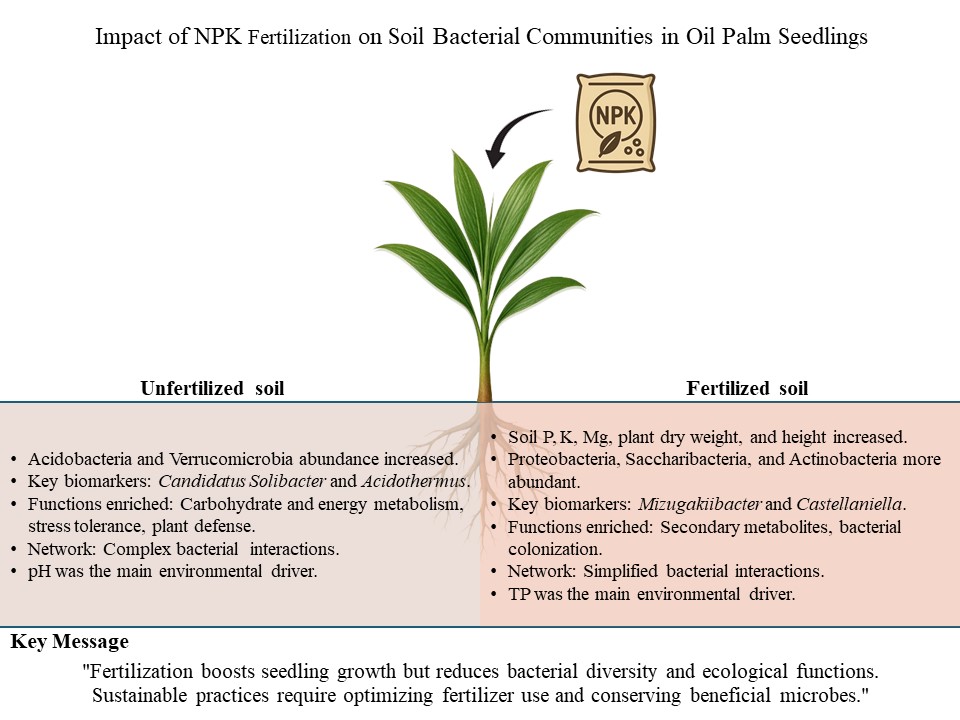
Malaysia's palm oil industry relies heavily on chemical fertilizers, leading to significant environmental concerns such as nutrient loss and declining biodiversity. This study aims to evaluate the impact of post-fertilizer application on bacterial communities in soil, particularly focusing on bulk soil and rhizosphere. Through amplicon sequencing, we investigated the response of bacterial diversity to unfertilized and NPK-fertilized soil treatments. Fertilizer application increased soil phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium levels, enhancing seedlings’ growth but reducing bacterial diversity, particularly sensitive groups such as Acidobacteria and Verrucomicrobia. Candidatus Solibacter and Acidothermus were consistent biomarkers for unfertilized soil, while Mizugakiibacter and Castellaniella were for fertilized treatment. For the inferred bacterial community functions, the unfertilized bulk soil demonstrated enhanced function related to carbohydrate metabolism, and the unfertilized rhizosphere exhibited functions related to energy metabolism, stress tolerance, bioremediation, and plant defense. During fertilized treatment, functions related to secondary metabolites were enriched in the bulk soil, and bacterial colonization functions were enriched in both compartments. For network analysis, the fertilizer application reduced bacterial network interactions and complexity. Environmental drivers, namely, pH and soil total phosphorus (TP), influenced the bacterial biomarkers' abundance in the bulk soil and rhizosphere. These findings demonstrate the need to optimize chemical fertilizer applications and identify beneficial bacterial taxa to foster sustainable agricultural practices in the palm oil industry.
Downloads
References
Abhauer, K. P., Wemheuer, B., Daniel, R., & Meinicke, P. (2015). Tax4Fun: predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics, 31(17), 2882-2884. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv287
Aerts, R., & Chapin III, F. S. (1999). The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a re-evaluation of processes and patterns. Advances in Ecological Research, 30, 1-67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60016-1
Ahmed, W., Jing, H., Kaillou, L., Qaswar, M., Khan, M. N., Jin, C., Geng, S., Qinghai, H., Yiren, L., Guangrong, L., Mei, S., Chao, L., Dongchu, L., Ali, S., Normatov, Y., Mehmood, S., & Zhang, H. (2019). Changes in phosphorus fractions associated with soil chemical properties under long-term organic and inorganic fertilization in paddy soils of southern China. PloS One, 14(5), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216881
Aizat, A. M., Roslan, M. K., Sulaiman, W. N. A., & Karam, D. S. (2014). The relationship between soil pH and selected soil properties in 48 years logged-over forest. International Journal of Environmental Sciences, 4(6), 1129-1140. https://doi.org/10.6088/ijes.2014040600004
Amjad, S. F., Mansoora, N., Yaseen, S., Kamal, A., Butt, B., Matloob, H., Alamri, S. A. M., Alrumman, S. A., Eid, E. M., & Shahbaz, M. (2021). Combined use of endophytic bacteria and pre-sowing treatment of thiamine mitigates the adverse effects of drought stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Sustainability, 13(12), 6582. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126582
Angelina, E., Papatheodorou, E. M., Demirtzoglou, T., & Monokrousos, N. (2020). Effects of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas fluorescens inoculation on attributes of the lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) soil rhizosphere microbial community: The role of the management system. Agronomy, 10(9), 1428. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091428
Antoun, H., Beauchamp, C. J., Goussard, N., Chabot, R., & Lalande, R. (1998). Potential of Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium species as plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on non-legumes: effect on radishes (Raphanus sativus L.). In Molecular Microbial Ecology of The Soil (pp. 57-67). Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-2321-3_5
Arifin, I., Hanafi, M. M., Roslan, I., Ubaydah, M. U., Abd Karim, Y., Tui, L. C., & Hamzah, S. (2022). Responses of irrigated oil palm to nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers on clayey soil. Agricultural Water Management, 274, 107922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107922
Arocha-Garza, H. F., Canales-Del Castillo, R., Eguiarte, L. E., Souza, V., & De la Torre-Zavala, S. (2017). High diversity and suggested endemicity of culturable Actinobacteria in an extremely oligotrophic desert oasis. PeerJ, 5, 1-21. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3247
Arora, P. K. (2020). Bacilli-mediated degradation of xenobiotic compounds and heavy metals. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 8, 570307. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.570307
Bai, L., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, X., Lu, Z., Zhang, D., Sun, F., & Zhao, X. (2022). Changes in the Microbial Community in Maize (Zea mays L.) Root Spatial Structure Following Short-Term Nitrogen Application. ACS Omega, 8(1), 208–218. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c01711
Banerjee, S., Schlaeppi, K., & van der Heijden, M. G. (2018). Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16(9), 567-576. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0024-1
Barabote, R. D., Xie, G., Leu, D. H., Normand, P., Necsulea, A., Daubin, V., Médigue, C., Adney, W. S., Xu, X. C., Lapidus, A., Parales, R. E., Detter, C., Pujic, P., Bruce, D., Lavire, C., Challacombe, J. F., Brettin, T. S., & Berry, A. M. (2009). Complete genome of the cellulolytic thermophile Acidothermus cellulolyticus 11B provides insights into its ecophysiological and evolutionary adaptations. Genome Research, 19(6), 1033-1043. http://www.genome.org/cgi/doi/10.1101/gr.084848.108
Barta, J., Tahovská, K., Šantrůčková, H., & Oulehle, F. (2017). Microbial communities with distinct denitrification potential in spruce and beech soils differing in nitrate leaching. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08554-1
Bei, S., Zhang, Y., Li, T., Christie, P., Li, X., & Zhang, J. (2018). Response of the soil microbial community to different fertilizer inputs in a wheat-maize rotation on a calcareous soil. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 260, 58-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.03.014
Belova, S. E., Ravin, N. V., Pankratov, T. A., Rakitin, A. L., Ivanova, A. A., Beletsky, A. V., Damste, J. S. S., & Dedysh, S. N. (2018). Hydrolytic capabilities as a key to environmental success: chitinolytic and cellulolytic Acidobacteria from acidic sub-arctic soils and boreal peatlands. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 2775. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02775
Berendsen, R. L., Pieterse, C. M., & Bakker, P. A. (2012). The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends in plant science, 17(8), 478-486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.04.001
Bertness, M. D., & Callaway, R. (1994). Positive interactions in communities. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 9(5), 191-193.
Berza, B., Sekar, J., Vaiyapuri, P., Pagano, M. C., & Assefa, F. (2022). Evaluation of inorganic phosphate solubilizing efficiency and multiple plant growth promoting properties of endophytic bacteria isolated from root nodules Erythrina brucei. BMC Microbiology, 22(1), 276. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-022-02688-7
Bolyen, E., Rideout, J. R., Dillon, M. R., Bokulich, N. A., Abnet, C. C., Al-Ghalith, G. A., Alexander, H., Alm, E. J., Arumugam, M., Asnicar, F., Bai, Y., Bisanz, J. E., Bittinger, K., Brejnrod, A., Brislawn, C. J., Brown, C. T., Callahan, B. J., Caraballo-Rodríguez, A. M., Chase, J., Cope, E. K., Da Silva, R., Diener, C., Dorrestein, P. C., Douglas, G. M., Durall, D. M., Duvallet, C., Edwardson, C. F., Ernst, M., Estaki, M., Fouquier, J., Gauglitz, J. M., Gibbon, S. M., Gibson, D. L., Gonzalez, A., Gorlick, K., Guo, J., Hillman, B., Holmes, S., Holste, H., Huttenhower, C., Huttley, G. A., Janssen, S., Jarmusch, A. K., Jiang, L., Kaehler, B. D., Kang, K. B., Keefe, C. R., Keim, P., Kelley, S. T., Knights, D., Koester, I., Kosciolek, T., Kreps, J., Langille, M. G. I., Lee, J., Ley, R., Liu, Y. X., Loftfield, E., Lazupone, C., Maher, M., Marotz, C., Martin, B. D., McDonald, D., Mclver, L. J., Melnik, A. V., Metcalf, J. L., Morgan, S. C., Morton, J. T., Naimey, A. T., Navas-Molina, J. A., Nothias, L. F., Orchanian, S. B., Pearson, T., Peoples, S. L., Petras, D., Preuss, M. L., Pruesse, E., Rasmussen, L. B., Rivers, A., Robeson II, M. S., Rosenthal, P., Segata, N., Shaffer, M., Shiffer, A., Sinha, R., Song, S. J., Spear, J. R., Swafford, A. D., Thompson, L. R., Torres, P. J., Trinh, P., Tripathi, A., Turnbaugh, P., J., Ul-Hasan, S., van der Hooft, J. J. J., Vargas, F., Vázquez-Baeza, Y., Vogtmann, E., von Hippel, M., Walters, W., Wan, Y., Wang, M., Warren, J., Weber, K. C., Williamson, C. H. D., Willis, A. D., Xu, Z., Z., Zaneveld, J. R., Zhang, Y., Zhu, Q., Knight, R., & Caporaso, J. G. (2019). Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nature Biotechnology, 37(8), 852-857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0252-6
Boubekri, K., Soumare, A., Mardad, I., Lyamlouli, K., Hafidi, M., Ouhdouch, Y., & Kouisni, L. (2021). The screening of potassium-and phosphate-solubilizing actinobacteria and the assessment of their ability to promote wheat growth parameters. Microorganisms, 9(3), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030470
Breitkreuz, C., Heintz-Buschart, A., Buscot, F., Wahdan, S. F. M., Tarkka, M., & Reitz, T. (2021). Can we estimate functionality of soil microbial communities from structure-derived predictions? A reality test in agricultural soils. Microbiology Spectrum, 9(1), 10-1128. https://doi.org/10.1128/Spectrum.00278-21
Bright, J. P., Baby, A. S., Thankappan, S., George, A. S., Maheshwari, H. S., Nataraj, R., Judson, S., & Binodh, A. K. (2022). Potassium releasing bacteria for unlocking soil potassium-a way forward for judicious use of chemical fertilizers. International Journal of Plant & Soil Science, 34, 49-61. https://doi.org/10.9734/IJPSS/2022/v34i1931088
Bunger, W., Jiang, X., Müller, J., Hurek, T., & Reinhold-Hurek, B. (2020). Novel cultivated endophytic Verrucomicrobia reveal deep-rooting traits of bacteria to associate with plants. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 8692. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65277-6
Caradonia, F., Ronga, D., Catellani, M., Giaretta Azevedo, C. V., Terrazas, R. A., Robertson-Albertyn, S., Francia, E., & Bulgarelli, D. (2019). Nitrogen fertilizers shape the composition and predicted functions of the microbiota of field-grown tomato plants. Phytobiomes Journal, 3(4), 315-325. https://doi.org/10.1094/PBIOMES-06-19-0028-R
Chen, L., Li, F., Li, W., Ning, Q., Li, J., Zhang, J., Ma, D., & Zhang, C. (2020). Organic amendment mitigates the negative impacts of mineral fertilization on bacterial communities in Shajiang black soil. Applied Soil Ecology, 150, 103457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.103457
Cheng, Y. F., Zhang, Z. Z., Li, G. F., Zhu, B. Q., Zhang, Q., Liu, Y. Y., Zhu, W. Q., Fan, N. S., & Jin, R. C. (2019). Effects of ZnO nanoparticles on high-rate denitrifying granular sludge and the role of phosphate in toxicity attenuation. Environmental Pollution, 251, 166-174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.138
Chhetri, G., Kang, M., Kim, J., Kim, I., So, Y., & Seo, T. (2021). Sphingosinicella flava sp. nov., indole acetic acid producing bacteria isolated from maize field soil. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 71(10), 005038. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.005038
Chong, J., Liu, P., Zhou, G., & Xia, J. (2020). Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nature Protocols, 15(3), 799-821. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0264-1
Csardi, G., & Nepusz, T. (2006). The igraph software package for complex network research. InterJournal Complex Systems, 1695(5), 1–9. http://igraph.sf.net
Cuhel, J., Malý, S., & Královec, J. (2019). Shifts and recovery of soil microbial communities in a 40-year field trial under mineral fertilization. Pedobiologia, 77, 150575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedobi.2019.150575
Dai, Z., Su, W., Chen, H., Barberán, A., Zhao, H., Yu, M., Yu, L., Brookes, P. C., Schadt, C. W., Chang, S. X., & Xu, J. (2018). Long‐term nitrogen fertilization decreases bacterial diversity and favors the growth of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria in agro‐ecosystems across the globe. Global Change Biology, 24(8), 3452-3461. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14163
David, D. J. (1960). The determination of exchangeable sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium in soils by atomic-absorption spectrophotometry. Analyst, 85(1012), 495-503.
Dedysh, S. N., & Damsté, J. S. S. (2018). Acidobacteria. eLS, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470015902.a0027685
Dennis, P. G., Miller, A. J., & Hirsch, P. R. (2010). Are root exudates more important than other sources of rhizodeposits in structuring rhizosphere bacterial communities?. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 72(3), 313-327. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.00860.x
DeSantis, T. Z., Hugenholtz, P., Larsen, N., Rojas, M., Brodie, E. L., Keller, K., Huber, T., Dalevi, D., Hu, P., & Andersen, G. L. (2006). Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(7), 5069-5072. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03006-05
Dhawi, F., Datta, R., & Ramakrishna, W. (2017). Proteomics provides insights into biological pathways altered by plant growth promoting bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhiza in sorghum grown in marginal soil. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Proteins and Proteomics, 1865(2), 243-251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.11.015
Dotaniya, M. L., Aparna, K., Dotaniya, C. K., Singh, M., & Regar, K. L. (2019). Role of soil enzymes in sustainable crop production. In Enzymes in Food Biotechnology (pp. 569-589). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813280-7.00033-5
Duncan, T. R., Werner-Washburne, M., & Northup, D. E. (2021). Diversity of Siderophore-Producing Bacterial Cultures From Carlsbad Caverns National Park (Ccnp) Caves, Carlsbad, New Mexico. Journal of Cave and Karst Studies: the National Speleological Society bulletin, 83(1), 29-43. https://doi.org/10.4311%2F2019es0118
Edgar, R. C. (2013). UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nature Methods, 10(10), 996-998. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2604
Eliot, C. H. (2011). Competition theory and channeling explanation. Philosophy, Theory, and Practice in Biology, 3 (20130604), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3998/ptb.6959004.0003.001
Esperschütz, J., Pérez-de-Mora, A., Schreiner, K., Welzl, G., Buegger, F., Zeyer, J., Hagedorn, F., Munch, J. C., & Schloter, M. (2011). Microbial food web dynamics along a soil chronosequence of a glacier forefield. Biogeosciences, 8(11), 3283-3294. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-8-3283-2011
Farrer, E. C., & Suding, K. N. (2016). Teasing apart plant community responses to N enrichment: the roles of resource limitation, competition and soil microbes. Ecology letters, 19(10), 1287-1296. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12665
Feng, C., Jia, J., Wang, C., Han, M., Dong, C., Huo, B., Li, D., & Liu, X. (2019). Phytoplankton and bacterial community structure in two chinese lakes of different trophic status. Microorganisms, 7(12), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7120621
Feng, Y., Delgado-Baquerizo, M., Zhu, Y., Han, X., Han, X., Xin, X., Li, W., Guo, Z., Dang, T., Li, C., Zhu, B., Cai, Z., Li, D., & Zhang, J. (2022). Responses of soil bacterial diversity to fertilization are driven by local environmental context across China. Engineering, 12, 164-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2021.09.012
Figueroa-Gonzalez, P. A., Bornemann, T. L., Adam, P. S., Plewka, J., Révész, F., Von Hagen, C. A., Táncsics, A., & Probst, A. J. (2020). Saccharibacteria as organic carbon sinks in hydrocarbon-fueled communities. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 587782. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.587782
Gao, L., Wang, R., Gao, J., Li, F., Huang, G., Huo, G., Liu, Z., Tang, W., & Shen, G. (2019). Analysis of the structure of bacterial and fungal communities in disease suppressive and disease conducive tobacco-planting soils in China. Soil Research, 58(1), 35-40. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR19204
Goecks, J., Nekrutenko, A., Taylor, J., Afgan, E., Ananda, G., Baker, D., Blankenberg, D., Chakrabarty, R., Coraor, N., Goecks, J., Von Kuster, G., Lazarus, R., Li, K., Taylor, J., & Vincent, K. (2010). Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biology, 11(8), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-r86
Goh, Y. K., Zoqratt, M. Z. H. M., Goh, Y. K., Ayub, Q., & Ting, A. S. Y. (2020). Determining soil microbial communities and their influence on Ganoderma disease incidences in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) via high-throughput sequencing. Biology, 9(12), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120424
Gomez-Garzon, C., Hernández-Santana, A., & Dussan, J. (2017). A genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of Lysinibacillus sphaericus unveils unexploited biotechnological potentials. PLoS One, 12(6), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0179666
Goulding, K. W. T. (2016). Soil acidification and the importance of liming agricultural soils with particular reference to the United Kingdom. Soil Use and Management, 32(3), 390-399. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12270
Gu, Y., Wang, Y., Lu, S. E., Xiang, Q., Yu, X., Zhao, K., Zou, L., Chen, Q., Tu, S., & Zhang, X. (2017). Long-term fertilization structures bacterial and archaeal communities along soil depth gradient in a paddy soil. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01516
Guo, N., Zhang, S., Gu, M., & Xu, G. (2021). Function, transport, and regulation of amino acids: What is missing in rice?. The Crop Journal, 9(3), 530-542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.04.002
Haiming, T., Xiaoping, X., Chao, L., Xiaochen, P., Kaikai, C., Weiyan, L., & Ke, W. (2020). Microbial carbon source utilization in rice rhizosphere and nonrhizosphere soils with short-term manure N input rate in paddy field. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 6487. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63639-8
Halifu, S., Deng, X., Song, X., An, Y., & Song, R. (2019). Effects of Sphaeropsis Blight on Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Physicochemical Properties of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica in Zhanggutai, China. Forests, 10(11), 1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10110954
Han, S. H., An, J. Y., Hwang, J., Kim, S. B., & Park, B. B. (2016). The effects of organic manure and chemical fertilizer on the growth and nutrient concentrations of yellow poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera Lin.) in a nursery system. Forest Science and Technology, 12(3), 137-143. https://doi.org/10.1080/21580103.2015.1135827
Havlin, J. L. (2005). Fertility. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment (pp. 10-19). Elsevier.
Heanes, D. L. (1981). Determination of trace elements in plant materials by a dry-ashing procedure. Part II. Copper, manganese and zinc. Analyst, 106(1259), 182-187. https://doi.org/10.1039/AN9810600172
Hernandez, D., Cardell, E., & Zarate, V. (2005). Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Tenerife cheese: initial characterization of plantaricin TF711, a bacteriocin‐like substance produced by Lactobacillus plantarum TF711. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 99(1), 77-84. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02576.x
Holland, B. L., Matthews, M. L., Bota, P., Sweetlove, L. J., Long, S. P., & diCenzo, G. C. (2023). A genome‐scale metabolic reconstruction of soybean and Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens reveals the cost–benefit of nitrogen fixation. New Phytologist. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.19203
Jaiswal, S. K., & Dakora, F. D. (2019). Widespread distribution of highly adapted Bradyrhizobium species nodulating diverse legumes in Africa. Frontiers in microbiology, 10, 310. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00310
Jamil, F., Mukhtar, H., Fouillaud, M., & Dufossé, L. (2022). Rhizosphere signaling: Insights into plant–rhizomicrobiome interactions for sustainable agronomy. Microorganisms, 10(5), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10050899
Ji, L., Xu, X., Zhang, F., Si, H., Li, L., & Mao, G. (2023). The Preliminary Research on Shifts in Maize Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities and Symbiotic Networks under Different Fertilizer Sources. Agronomy, 13(8), 2111. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13082111
Kakar, K., Xuan, T. D., & Khanh, T. D. (2023). Allelopathic Potential of Sweet Sorghum Root Exudates and Identification of the Relevant Allelochemicals. Agrochemicals, 2(1), 96-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/agrochemicals2010007
Kalam, S., Basu, A., Ahmad, I., Sayyed, R. Z., El Enshasy, H. A., Dailin, D. J., & Suriani, N. (2020). Recent understanding of soil Acidobacteria and their ecological significance: A critical review. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.580024
Kandel, S., Kim, Y., Park, J., & Lee, J. (2019). Nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization effects on bacterial community structure and functional gene diversity of the rice rhizosphere. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 1498.
Kathiravan, A., & Gnanadoss, J. J. (2021). White-rot fungi-mediated bioremediation as a sustainable method for xenobiotic degradation. Environmental and Experimental Biology, 19(3), 103-119. https://doi.org/10.22364/eeb.19.11
Kavvadias, V., Ioannou, Z., Vavoulidou, E., & Paschalidis, C. (2023). Short Term Effects of Chemical Fertilizer, Compost and Zeolite on Yield of Lettuce, Nutrient Composition and Soil Properties. Agriculture, 13(5), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13051022
Kim, C., Baek, G., Yoo, B. O., Jung, S. Y., & Lee, K. S. (2018). Regular fertilization effects on the nutrient distribution of bamboo components in a moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens (Mazel) Ohwi) stand in South Korea. Forests, 9(11), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9110671
Kim, S. K., Chung, D., Himmel, M. E., Bomble, Y. J., & Westpheling, J. (2016). Heterologous expression of family 10 xylanases from Acidothermus cellulolyticus enhances the exoproteome of Caldicellulosiruptor bescii and growth on xylan substrates. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 9, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0588-9
Kojima, H., Tokizawa, R., & Fukui, M. (2014). Mizugakiibacter sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a freshwater lake. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 64(Pt_12), 3983-3987. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.064659-0
Kramer, S., Dibbern, D., Moll, J., Huenninghaus, M., Koller, R., Krueger, D., Marhan, S., Urich, T., Wubet, T., Bonkowski, M., Buscot, F., Leuders, T., & Kandeler, E. (2016). Resource partitioning between bacteria, fungi, and protists in the detritusphere of an agricultural soil. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01524
Kumawat, K. C., Sharma, P., Sirari, A., Singh, I., Gill, B. S., Singh, U., & Saharan, K. (2019). Synergism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (LSE-2) nodule endophyte with Bradyrhizobium sp. (LSBR-3) for improving plant growth, nutrient acquisition and soil health in soybean. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 35(3), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2622-0
Legendre, P., & Gallagher, E. D. (2001). Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia, 129, 271-280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100716
Lewis, R. W., Barth, V. P., Coffey, T., McFarland, C., Huggins, D. R., & Sullivan, T. S. (2018). Altered bacterial communities in long-term no-till soils associated with stratification of soluble aluminum and soil pH. Soil Systems, 2(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/soils2010007
Li, F., Chen, L., Zhang, J., Yin, J., & Huang, S. (2017). Bacterial community structure after long-term organic and inorganic fertilization reveals important associations between soil nutrients and specific taxa involved in nutrient transformations. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00187
Li, K., Han, X., Ni, R., Shi, G., De-Miguel, S., Li, C., Shen, W., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, X. (2021). Impact of Robinia pseudoacacia stand conversion on soil properties and bacterial community composition in Mount Tai, China. Forest Ecosystems, 8(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-021-00296-x
Lin, S. Y., Hameed, A., Hsieh, Y. T., Hsu, Y. H., Lai, W. A., & Young, C. C. (2018). Castellaniella fermenti sp. nov., isolated from a fermented meal. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 68(1), 52-57. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002436
Lin, W., Lin, M., Zhou, H., Wu, H., Li, Z., & Lin, W. (2019). The effects of chemical and organic fertilizer usage on rhizosphere soil in tea orchards. PloS One, 14(5), e0217018. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217018
Liu, C., Gong, X., Dang, K., Li, J., Yang, P., Gao, X., Deng, X., & Feng, B. (2020b). Linkages between nutrient ratio and the microbial community in rhizosphere soil following fertilizer management. Environmental Research, 184, 109261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109261
Liu, J., Ma, Q., Hui, X., Ran, J., Ma, Q., Wang, X., & Wang, Z. (2020a). Long-term high-P fertilizer input decreased the total bacterial diversity but not phoD-harboring bacteria in wheat rhizosphere soil with available-P deficiency. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 149, 107918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107918
Liu, K., Cai, M., Hu, C., Sun, X., Cheng, Q., Jia, W., Yang, T., Nie, M., & Zhao, X. (2019). Selenium (Se) reduces Sclerotinia stem rot disease incidence of oilseed rape by increasing plant Se concentration and shifting soil microbial community and functional profiles. Environmental Pollution, 254, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113051
Loutet, S. A., Chan, A. C., Kobylarz, M. J., Verstraete, M. M., Pfaffen, S., Ye, B., Arrieta, A. L., & Murphy, M. E. (2021). The fate of intracellular metal ions in microbes.
Lu, X., Heal, K. R., Ingalls, A. E., Doxey, A. C., & Neufeld, J. D. (2020). Metagenomic and chemical characterization of soil cobalamin production. The ISME Journal, 14(1), 53-66. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-019-0502-0
Ma, L., Pang, A. P., Luo, Y., Lu, X., & Lin, F. (2020). Beneficial factors for biomineralization by ureolytic bacterium Sporosarcina pasteurii. Microbial Cell Factories, 19(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-1281-z
Magoč, T., & Salzberg, S. L. (2011). FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 27(21), 2957-2963. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507
Malaysian Standard [MS] (1980). MS 678–Recommended methods for soil chemical analysis: Part I–V. Shah Alam: Standards and Industrial Research Institute of Malaysia.
Mallhi, Z. I., Rizwan, M., Mansha, A., Ali, Q., Asim, S., Ali, S., Hussain, A., Alrokayan, S. H., Khan, H. A., Alam, P., & Ahmad, P. (2019). Citric acid enhances plant growth, photosynthesis, and phytoextraction of lead by alleviating the oxidative stress in castor beans. Plants, 8(11), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8110525
Mandakovic, D., Aguado-Norese, C., García-Jiménez, B., Hodar, C., Maldonado, J. E., Gaete, A., Latorre, M., Wilkinson, M. D., Gutiérrez, R. A., Cavierres, L. A., Medina, J., Cambiazo, V., & Gonzalez, M. (2023). Testing the stress gradient hypothesis in soil bacterial communities associated with vegetation belts in the Andean Atacama Desert. Environmental Microbiome, 18(1), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40793-023-00486-w
Mao, X., Xu, X., Lu, K., Gielen, G., Luo, J., He, L., Donnison, A., Xu, Z., Xu, J., Yang, W., Song, Z., & Wang, H. (2015). Effect of 17 years of organic and inorganic fertilizer applications on soil phosphorus dynamics in a rice–wheat rotation cropping system in eastern China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 15(9), 1889-1899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1137-z
Matejovic, I. (1993). Determination of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen in soils by automated elemental analysis (dry combustion method). Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 24(17-18), 2213-2222. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629309368950
McDonald, D., Price, M. N., Goodrich, J., Nawrocki, E. P., DeSantis, T. Z., Probst, A., Andersen, G. L., Knight, R., & Hugenholtz, P. (2012). An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. The ISME Journal, 6(3), 610-618. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.139
McMurdie, P. J., & Holmes, S. (2013). Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS One, 8(4), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061217
McNear Jr., D. H. (2013) The Rhizosphere - Roots, Soil and Everything In Between. Nature Education Knowledge 4(3), 1. https://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/the-rhizosphere-roots-soil-and-67500617/ (accessed 22 February 2023)
Merchant, S. S., & Helmann, J. D. (2012). Elemental economy: microbial strategies for optimizing growth in the face of nutrient limitation. Advances in Microbial Physiology, 60, 91-210. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-398264-3.00002-4
Morcillo, R. J., & Manzanera, M. (2021). The effects of plant-associated bacterial exopolysaccharides on plant abiotic stress tolerance. Metabolites, 11(6), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060337
Morigasaki, S., Matsui, M., Ohtsu, I., Doi, Y., Kawano, Y., Nakai, R., Iwasaki, W., Hayashi, H., & Takaya, N. (2024). Temporal and fertilizer-dependent dynamics of soil bacterial communities in buckwheat fields under long-term management. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 9896. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60655-w
MPOB (2022a). Malaysian Oil Palm Statistics 2021. 41st edition. MPOB, Bangi
MPOB (2022b). Review of the Malaysian Oil Palm Industry 2021. MPOB, Bangi.
Murphy, D. J., Goggin, K., & Paterson, R. R. M. (2021). Oil palm in the 2020s and beyond: challenges and solutions. CABI Agriculture and Bioscience, 2(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43170-021-00058-3
Ndabankulu, K., Egbewale, S. O., Tsvuura, Z., & Magadlela, A. (2022). Soil microbes and associated extracellular enzymes largely impact nutrient bioavailability in acidic and nutrient poor grassland ecosystem soils. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 12601. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16949-y
Ng, J. F., Ahmed, O. H., Jalloh, M. B., Omar, L., Kwan, Y. M., Musah, A. A., & Poong, K. H. (2022). Soil nutrient retention and pH buffering capacity are enhanced by calciprill and sodium silicate. Agronomy, 12(1), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12010219
Noble, A. S., Noe, S., Clearwater, M. J., & Lee, C. K. (2020). A core phyllosphere microbiome exists across distant populations of a tree species indigenous to New Zealand. PLoS One, 15(8), e0237079. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0237079
O’Brien, F. J., Dumont, M. G., Webb, J. S., & Poppy, G. M. (2018). Rhizosphere bacterial communities differ according to fertilizer regimes and cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) harvest time, but not aphid herbivory. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01620
Ogola, H. J. O., Selvarajan, R., & Tekere, M. (2021). Local geomorphological gradients and land use patterns play key role on the soil bacterial community diversity and dynamics in the highly endemic indigenous afrotemperate coastal scarp forest biome. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 592725. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.592725
Oksanen, J. (2015). Vegan: an introduction to ordination. URL http://cran. r-project. org/web/packages/vegan/vignettes/introvegan. pdf, 8, 1-19.
Parks, D. H., Tyson, G. W., Hugenholtz, P., & Beiko, R. G. (2014). STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics, 30(21), 3123–3124. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu494
Piccoli, P., & Bottini, R. (2013). Terpene production by bacteria and its involvement in plant growth promotion, stress alleviation, and yield increase. Molecular Microbial Ecology of the Rhizosphere, 1, 335-343. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118297674.ch31
Pirker, J., Mosnier, A., Kraxner, F., Havlík, P., & Obersteiner, M. (2016). What are the limits to oil palm expansion? Global Environmental Change, 40, 73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.06.007
Price, G. W., Langille, M. G., & Yurgel, S. N. (2021). Microbial co-occurrence network analysis of soils receiving short-and long-term applications of alkaline treated biosolids. Science of The Total Environment, 751, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141687
Qiu, L., Zhang, Q., Zhu, H., Reich, P. B., Banerjee, S., van der Heijden, M. G. A., Sadowsky, M. J., Ishii, S., Jia, X., Shao, M., Liu, B., Jiao, H., Li, H., & Wei, X. (2021). Erosion reduces soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality. The ISME Journal, 15(8), 2474-2489. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-00913-1
Quast, C., Pruesse, E., Yilmaz, P., Gerken, J., Schweer, T., Yarza, P., Peplies, J., & Glöckner, F. O. (2012). The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(D1), D590-D596. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1219
Rawat, S. R., Männistö, M. K., Bromberg, Y., & Häggblom, M. M. (2012). Comparative genomic and physiological analysis provides insights into the role of Acidobacteria in organic carbon utilization in Arctic tundra soils. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 82(2), 341-355. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2012.01381.x
Ren, D., Madsen, J. S., Sørensen, S. J., & Burmølle, M. (2015). High prevalence of biofilm synergy among bacterial soil isolates in cocultures indicates bacterial interspecific cooperation. The ISME Journal, 9(1), 81-89. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.96
Ren, H., Wang, H., Qi, X., Yu, Z., Zheng, X., Zhang, S., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Ahmed, T., & Li, B. (2021). The damage caused by decline disease in bayberry plants through changes in soil properties, rhizosphere microbial community structure and metabolites. Plants, 10(10), 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102083
Ren, M., Zhang, Z., Wang, X., Zhou, Z., Chen, D., Zeng, H., Zhao, S., Chen, L., Hu, Y., Zhang, C., Liang, Y., She, Q., Zhang, Y., & Peng, N. (2018). Diversity and contributions to nitrogen cycling and carbon fixation of soil salinity shaped microbial communities in Tarim Basin. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00431
Sakoula, D., Koch, H., Frank, J., Jetten, M. S., van Kessel, M. A., & Lücker, S. (2021). Enrichment and physiological characterization of a novel comammox Nitrospira indicates ammonium inhibition of complete nitrification. The ISME Journal, 15(4), 1010-1024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-00827-4
Segata, N., Izard, J., Waldron, L., Gevers, D., Miropolsky, L., Garrett, W. S., & Huttenhower, C. (2011). Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biology, 12(6), 1–18. https://doi.org/doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60
Selim, M. S. M., Abdelhamid, S. A., & Mohamed, S. S. (2021). Secondary metabolites and biodiversity of actinomycetes. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 19(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-021-00156-9
Semenov, M. V., Krasnov, G. S., Semenov, V. M., & van Bruggen, A. H. (2020). Long-term fertilization rather than plant species shapes rhizosphere and bulk soil prokaryotic communities in agroecosystems. Applied Soil Ecology, 154, 103641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103641
Seraj, M. F., Rahman, T., Lawrie, A. C., & Reichman, S. M. (2020). Assessing the plant growth promoting and arsenic tolerance potential of Bradyrhizobium japonicum CB1809. Environmental Management, 66(5), 930-939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-020-01351-z
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang, J. T., Ramage, D., Amin, N., Schwikowski, B., & Ideker, T. (2003). Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models. Genome Research, 13(11), 24980–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303.metabolite
Shen, G., Zhang, S., Liu, X., Jiang, Q., & Ding, W. (2018). Soil acidification amendments change the rhizosphere bacterial community of tobacco in a bacterial wilt affected field. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102, 9781-9791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9347-0
Shi, Y., Qiu, L., Guo, L., Man, J., Shang, B., Pu, R., Ou, X., Dai, C., Liu, P., Yang, Y., & Cui, X. (2020). K fertilizers reduce the accumulation of Cd in Panax notoginseng (Burk.) FH by improving the quality of the microbial community. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11, 888. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00888
Singh, B. K., Jha, B., Tripathi, S., Singh, D. K., & Trivedi, P. (2018). Impact of long-term fertilizer application on rhizosphere bacterial community structure of wheat and barley. MicrobiologyOpen, 7(5), e00637.
Sinong, G. F., Yasuda, M., Nara, Y., Lee, C. G., Dastogeer, K. M. G., Tabuchi, H., Nakai, H., Djedidi, S., & Okazaki, S. (2021). Distinct root microbial communities in nature farming rice harbor bacterial strains with plant growth-promoting traits. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 4, 629942. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2020.629942
Song, J., Min, L., Wu, J., He, Q., Chen, F., & Wang, Y. (2021). Response of the microbial community to phosphate-solubilizing bacterial inoculants on Ulmus chenmoui Cheng in Eastern China. Plos One, 16(2), e0247309. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0247309
Su, X., Li, S., Cai, J., Xiao, Y., Tao, L., Hashmi, M. Z., Lin, H., Chen, J., Mei, R., & Sun, F. (2019). Aerobic degradation of 3, 3′, 4, 4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl by a resuscitated strain Castellaniella sp. SPC4: kinetics model and pathway for biodegradation. Science of the Total Environment, 688, 917-925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.364
Svenningsen, N. B., Watts-Williams, S. J., Joner, E. J., Battini, F., Efthymiou, A., Cruz-Paredes, C., Nybroe, O., & Jakobsen, I. (2018). Suppression of the activity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi by the soil microbiota. The ISME Journal, 12(5), 1296-1307. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-018-0059-3
Tandon, H. L. S., Cescas, M. P., & Tyner, E. H. (1968). An acid‐free vanadate‐molybdate reagent for the determination of total phosphorus in soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 32(1), 48-51. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1968.03615995003200010012x
Tang, S., Zhou, J., Pan, W., Sun, T., Liu, M., Tang, R., Li, Z., Ma, Q., & Wu, L. (2023). Effects of combined application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers on tea (Camellia sinensis) growth and fungal community. Applied Soil Ecology, 181, 104661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2022.104661
Tarmizi, A. M., & Mohd Tayeb, D. (2006). Nutrient demands of tenera oil palm planted on inland soil of Malaysia. Journal of Oil Palm Research, 18, 204.
Tebo, B. M., Davis, R. E., Anitori, R. P., Connell, L. B., Schiffman, P., & Staudigel, H. (2015). Microbial communities in dark oligotrophic volcanic ice cave ecosystems of Mt. Erebus, Antarctica. Frontiers In Microbiology, 6, 179. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00179
Tkaczyk, P., Mocek-Płóciniak, A., Skowrońska, M., Bednarek, W., Kuśmierz, S., & Zawierucha, E. (2020). The mineral fertilizer-dependent chemical parameters of soil acidification under field conditions. Sustainability, 12(17), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177165
van der Ploeg, R. R., Böhm, W., & Kirkham, M. B. (1999). On the origin of the theory of mineral nutrition of plants and the law of the minimum. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 63(5), 1055-1062. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1999.6351055x
Verma, P., & Rawat, S. (2021). Rhizoremediation of heavy metal-and xenobiotic-contaminated soil: an eco-friendly approach. Removal of Emerging Contaminants Through Microbial Processes, 95-113. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5901-3_5
Vives-Peris, V., De Ollas, C., Gómez-Cadenas, A., & Pérez-Clemente, R. M. (2020). Root exudates: from plant to rhizosphere and beyond. Plant Cell Reports, 39, 3-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02447-5
Wang, M., Xu, Y., Ni, H., Ren, S., Li, N., Wu, Y., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, Y., Shi, J., Zhang, Y., Jiang, L., & Tu, Q. (2023). Effect of fertilization combination on cucumber quality and soil microbial community. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14, 1122278. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1122278
Wang, Q., Jiang, X., Guan, D., Wei, D., Zhao, B., Ma, M., Chen, S., Li, L., Cao, F., & Li, J. (2018). Long-term fertilization changes bacterial diversity and bacterial communities in the maize rhizosphere of Chinese Mollisols. Applied Soil Ecology, 125, 88-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.12.007
Wang, W., Yang, Y., Li, J., Bu, P., Lu, A., Wang, H., He, W., Bermudez, R. S., & Feng, J. (2024). Consecutive Fertilization-Promoted Soil Nutrient Availability and Altered Rhizosphere Bacterial and Bulk Fungal Community Composition. Forests, 15(3), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030514
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, X., Wang, S., & Zhou, J. (2015). Nitrogen fertilization alters bacterial community structure and diversity in the soybean rhizosphere. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81(20), 7113-7121.
Wanke, A., Malisic, M., Wawra, S., & Zuccaro, A. (2021). Unraveling the sugar code: the role of microbial extracellular glycans in plant–microbe interactions. Journal of Experimental Botany, 72(1), 15-35. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa414
Ward, N. L., Challacombe, J. F., Janssen, P. H., Henrissat, B., Coutinho, P. M., Wu, M., Xie, G., Haft, D. H., Sait, M., Badger, J., Barabote, R. D., Bradley, B., Brettin, T. S., Brinkac, L. M., Bruce, D., Creasy, T., Daugherty, S. C., Davidsen, T. M., DeBoy, R. T., Detter, J. C., Dodson, R. J., Durkin, A. S., Ganapathy, A., Gwinn-Giglio, M., Han, C. S., Khouri, H., Kiss, H., Kothari, S. P., Madupu, R., Nelson, K. E., Nelson, W. C., Paulsen, I., Penn, K., Ren, Q., Rosovitz, M. J., Selengut, J. D., Shrivastava, S., Sullivan, S. A., Tapia, R., Thompson, L. S., Watkins, K. L., Yang, Q., Yu, C., Zafar, N., Zhou, L., & Kuske, C. R. (2009). Three genomes from the phylum Acidobacteria provide insight into the lifestyles of these microorganisms in soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75(7), 2046-2056. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02294-08
Wei, W., Yang, M., Liu, Y., Huang, H., Ye, C., Zheng, J., Guo, C., Hao, M., He, X., & Zhu, S. (2018). Fertilizer N application rate impacts plant-soil feedback in a sanqi production system. Science of the Total Environment, 633, 796-807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.219
Wen, T., Yu, G. H., Hong, W. D., Yuan, J., Niu, G. Q., Xie, P. H., Sun, F. S., Guo, L. D., Kuzyakov, Y., & Shen, Q. R. (2022). Root exudate chemistry affects soil carbon mobilization via microbial community reassembly. Fundamental Research, 2(5), 697-707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fmre.2021.12.016
Wieland, G., Neumann, R., & Backhaus, H. (2001). Variation of Microbial Communities in Soil, Rhizosphere, and Rhizoplane in Response to Crop Species, Soil Type, and Crop Development. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(12), 5849–5854. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.12.5849-5854.2001
Wu, W., Wang, X., Ren, Z., Zhou, X., & Du, G. (2022). N-Induced Species Loss Dampened by Clipping Mainly Through Suppressing Dominant Species in an Alpine Meadow. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13, 815011. https://doi.org/10.3389%2Ffpls.2022.815011
Xu, A., Li, L., Xie, J., Zhang, R., Luo, Z., Cai, L., Liu, C., Wang, L., Anwar, S., & Jiang, Y. (2022). Bacterial Diversity and Potential Functions in Response to Long-Term Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Semiarid Loess Plateau. Microorganisms, 10(8), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10081579
Xu, Q., Ling, N., Chen, H., Duan, Y., Wang, S., Shen, Q., & Vandenkoornhuyse, P. (2020). Long-term chemical-only fertilization induces a diversity decline and deep selection on the soil bacteria. Msystems, 5(4), e00337-20. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00337-20
Yang, L., Sun, R., Li, J., Zhai, L., Cui, H., Fan, B., Wang, H., & Liu, H. (2023). Combined organic-inorganic fertilization builds higher stability of soil and root microbial networks than exclusive mineral or organic fertilization. Soil Ecology Letters, 5(2), 220142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42832-022-0142-6
Yang, L., Sun, R., Li, J., Zhai, L., Cui, H., Fan, B., Wang, H., & Liu, H. (2021). Organic-inorganic fertilization built higher stability of soil and root microbial networks than exclusive mineral or organic fertilization. ResearchSquare, 1-26. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-652488/v1
Yin, X., Li, T., Jiang, X., Tang, X., Zhang, J., Yuan, L., & Wei, Y. (2022). Suppression of grape white rot caused by Coniella vitis using the potential biocontrol agent Bacillus Velezensis GSBZ09. Pathogens, 11(2), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020248
Yu, Z., Hu, X., Wei, D., Liu, J., Zhou, B., Jin, J., Liu, X., & Wang, G. (2019). Long-term inorganic fertilizer use influences bacterial communities in Mollisols of Northeast China based on high-throughput sequencing and network analyses. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science. 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2018.1563685
Zegeye, E. K., Brislawn, C. J., Farris, Y., Fansler, S. J., Hofmockel, K. S., Jansson, J. K., Wright, A. T., Graham, E. B., Naylor, D., McClure, R. S., & Bernstein, H. C. (2019). Selection, succession, and stabilization of soil microbial consortia. Msystems, 4(4), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00055-19
Zhang, C., Song, Z., Zhuang, D., Wang, J., Xie, S., & Liu, G. (2019a). Urea fertilization decreases soil bacterial diversity, but improves microbial biomass, respiration, and N-cycling potential in a semiarid grassland. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 55(3), 229-242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-019-01344-z
Zhang, Q., Li, Y., He, Y., Liu, H., Dumont, M. G., Brookes, P. C., & Xu, J. (2019b). Nitrosospira cluster 3-like bacterial ammonia oxidizers and Nitrospira-like nitrite oxidizers dominate nitrification activity in acidic terrace paddy soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 131, 229-237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.01.006
Zhao, F., Guo, X. Q., Wang, P., He, L. Y., Huang, Z., & Sheng, X. F. (2013). Dyella jiangningensis sp. nov., a γ-proteobacterium isolated from the surface of potassium-bearing rock. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 63(Pt_9), 3154-3157. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.048470-0
Zhao, Z., Zhao, R., Qiu, X., Wan, Y., & Lee, L. (2022). Structural Diversity of Bacterial Communities and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in the Surface Sediments from Main Stream of Qingshui River. Water, 14(21), 3356. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213356
Zheng, B. X., Bi, Q. F., Hao, X. L., Zhou, G. W., & Yang, X. R. (2017). Massilia phosphatilytica sp. nov., a phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from a long-term fertilized soil. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 67(8), 2514-2519. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001916
Zhou, J., Jiang, X., Zhou, B., Zhao, B., Ma, M., Guan, D., Li, J., Chen, S., Cao, F., Shen, D., & Qin, J. (2016). Thirty four years of nitrogen fertilization decreases fungal diversity and alters fungal community composition in black soil in northeast China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 95, 135-143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.12.012
Zhou, Z., Tran, P. Q., Kieft, K., & Anantharaman, K. (2020). Genome diversification in globally distributed novel marine Proteobacteria is linked to environmental adaptation. The ISME Journal, 14(8), 2060-2077. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-0669-4
Zhou, Z., Yan, T., Zhu, Q., Bu, X., Chen, B., Xue, J., & Wu, Y. (2019). Bacterial community structure shifts induced by biochar amendment to karst calcareous soil in southwestern areas of China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19, 356-365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2035-y
Zhu, S., Vivanco, J. M., & Manter, D. K. (2016). Nitrogen fertilizer rate affects root exudation, the rhizosphere microbiome and nitrogen-use-efficiency of maize. Applied Soil Ecology, 107, 324-333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.07.009
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Malaysian Journal of Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Transfer of Copyrights
- In the event of publication of the manuscript entitled [INSERT MANUSCRIPT TITLE AND REF NO.] in the Malaysian Journal of Science, I hereby transfer copyrights of the manuscript title, abstract and contents to the Malaysian Journal of Science and the Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publisher) for the full legal term of copyright and any renewals thereof throughout the world in any format, and any media for communication.
Conditions of Publication
- I hereby state that this manuscript to be published is an original work, unpublished in any form prior and I have obtained the necessary permission for the reproduction (or am the owner) of any images, illustrations, tables, charts, figures, maps, photographs and other visual materials of whom the copyrights is owned by a third party.
- This manuscript contains no statements that are contradictory to the relevant local and international laws or that infringes on the rights of others.
- I agree to indemnify the Malaysian Journal of Science and the Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publisher) in the event of any claims that arise in regards to the above conditions and assume full liability on the published manuscript.
Reviewer’s Responsibilities
- Reviewers must treat the manuscripts received for reviewing process as confidential. It must not be shown or discussed with others without the authorization from the editor of MJS.
- Reviewers assigned must not have conflicts of interest with respect to the original work, the authors of the article or the research funding.
- Reviewers should judge or evaluate the manuscripts objective as possible. The feedback from the reviewers should be express clearly with supporting arguments.
- If the assigned reviewer considers themselves not able to complete the review of the manuscript, they must communicate with the editor, so that the manuscript could be sent to another suitable reviewer.
Copyright: Rights of the Author(s)
- Effective 2007, it will become the policy of the Malaysian Journal of Science (published by the Faculty of Science, University of Malaya) to obtain copyrights of all manuscripts published. This is to facilitate:
- Protection against copyright infringement of the manuscript through copyright breaches or piracy.
- Timely handling of reproduction requests from authorized third parties that are addressed directly to the Faculty of Science, University of Malaya.
- As the author, you may publish the fore-mentioned manuscript, whole or any part thereof, provided acknowledgement regarding copyright notice and reference to first publication in the Malaysian Journal of Science and Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publishers) are given. You may produce copies of your manuscript, whole or any part thereof, for teaching purposes or to be provided, on individual basis, to fellow researchers.
- You may include the fore-mentioned manuscript, whole or any part thereof, electronically on a secure network at your affiliated institution, provided acknowledgement regarding copyright notice and reference to first publication in the Malaysian Journal of Science and Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publishers) are given.
- You may include the fore-mentioned manuscript, whole or any part thereof, on the World Wide Web, provided acknowledgement regarding copyright notice and reference to first publication in the Malaysian Journal of Science and Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publishers) are given.
- In the event that your manuscript, whole or any part thereof, has been requested to be reproduced, for any purpose or in any form approved by the Malaysian Journal of Science and Faculty of Science, University of Malaya (as the publishers), you will be informed. It is requested that any changes to your contact details (especially e-mail addresses) are made known.
Copyright: Role and responsibility of the Author(s)
- In the event of the manuscript to be published in the Malaysian Journal of Science contains materials copyrighted to others prior, it is the responsibility of current author(s) to obtain written permission from the copyright owner or owners.
- This written permission should be submitted with the proof-copy of the manuscript to be published in the Malaysian Journal of Science
Licensing Policy
Malaysian Journal of Science is an open-access journal that follows the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0)
CC BY – NC 4.0: Under this licence, the reusers to distribute, remix, alter, and build upon the content in any media or format for non-commercial purposes only, as long as proper acknowledgement is given to the authors of the original work. Please take the time to read the whole licence agreement (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode ).





